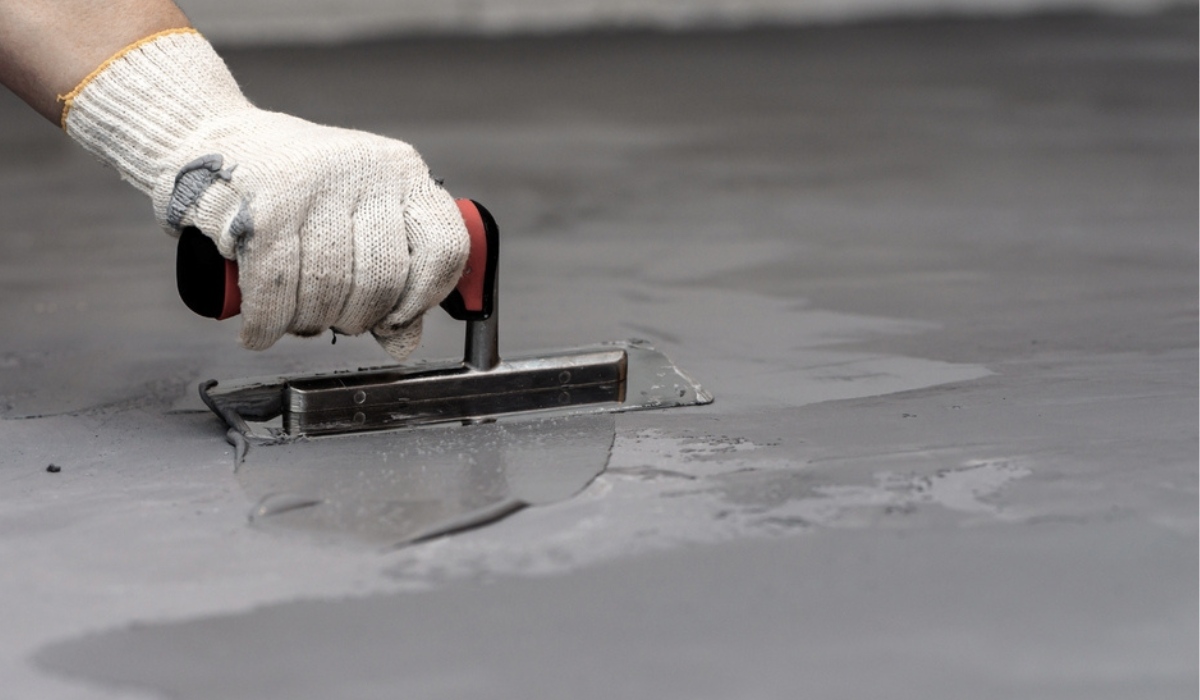
What Are the Benefits of Concrete?
Concreting Melbourne is an exceptionally tough material that can withstand even extreme temperatures and harsh elements, making it an excellent choice for construction in warmer and drier climates.
Concrete buildings feature minimal air infiltration, helping reduce disease-causing contaminants spreading throughout their interior spaces and their soundproofing features protecting residents from noise pollution.
Durability
Concrete stands up well under harsh environments that would otherwise wreak havoc on other structures, which is why it’s such a popular construction material. Concrete resists fire, wind and water damage as well as seismic vibrations; unlike steel and wood which require frequent coating replacements to stay functional over time.
Concrete can also be utilized as an effective sound and vibration buffer in medical facilities, where too much noise could hinder patient recovery or stress staff members performing delicate procedures.
Also, industrial byproducts like fly ash and silica fume can be added to concrete mixes to improve certain qualities, including durability. This approach is more environmentally-friendly as it uses waste materials while cutting costs overall.
Strength
Concrete has an extremely high compressive strength but a significantly lower tensile strength; therefore structures subject to tension should be reinforced using steel reinforcement bars or similar materials with greater tensional strength than concrete. Concrete’s strength depends on how much water was added relative to cement used and factors like aggregate grading size shape texture etc.
To achieve greater strength, most concrete mixtures incorporate one or more additional cementitious materials such as fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag, silica fume and metakaolin into their ingredients list. These additives enhance fresh properties as well as durability in concrete.
Concrete’s strength makes fighting fires faster and safer; as it doesn’t burn, melt or release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This is an enormous benefit in residential construction where VOCs may pose health hazards.
Flexibility
Concrete’s versatile nature enables it to be easily formed into different shapes and forms, which makes it particularly suitable for high-rise construction projects and allows builders to customize structures while maintaining strength and durability.
Concrete is often used in building the framework for buildings from their foundations upward, including floors and walls. Additionally, it is popularly employed on pavements and motorways where its strength makes it suitable to handle vehicle traffic loads.
Buildings constructed using concrete can become more energy-efficient when using this material to absorb and retain heat. Concrete also helps reduce noise and vibration levels within buildings – an advantage especially beneficial in hospitals or private practices where patients and staff require silence in order to focus.
Recyclability
Concrete is a long-lasting yet adaptable building material, with incredible versatility for reuse in multiple settings and environments. Concrete’s ability to be recycled helps save natural resources while simultaneously decreasing greenhouse gases emissions into our atmosphere.
Fly ash, ground vehicle tires and granulated blast furnace slag can all be utilized in concrete production to reduce environmental impact while simultaneously improving properties such as compressive strength and freeze-thaw resistance of concrete products. This approach not only saves landfill space but can be an economical way of producing high quality concrete that meets environmental sustainability targets.
Concrete recycling can also save construction companies money in terms of disposal fees and transportation costs, by recycling their own debris on-site for use in their concrete mix. Furthermore, this helps them comply with landfill regulations and avoid run-ins with local authorities.
Sustainability
Concrete is an environmentally-friendly building material, as it won’t rust, mildew or attract insects like other materials do. Furthermore, its insulation properties reduce energy use while keeping buildings cooler resulting in savings on heating and cooling bills.
Concrete’s durability means it can last decades without needing repair or replacement costs, saving both money and resources required for cleaning and upkeep. Furthermore, its minimal maintenance requirements save on resources for cleaning and caretaking costs.
Concrete construction sites utilize aggregate materials sourced within 160km of their construction sites, minimizing transportation emissions and pollution while mitigating environmental impact. Furthermore, its production process utilizes recycled materials – from industrial by-products such as scrap tyres to the recycled content used during production – all part of a circular economy approach by industry players.